Cross layer filtering with GeoServer¶
Normal GeoServer operation allows a filter to be applied on each layer in isolation, based on its attribute and external information (geometry, values) provided by the user. Cross layer filtering is instead the ability to select features from one layer that bear some relationship with features coming from another layer. Common questions that cross layer filters can help answering are:
- find all the ice cream stores located in a public park (point vs polygon)
- find all bus stops within 100m from the National Bank subsidiaries (point vs point, with distance reference)
- find all coastal roads (line VS polygon, assuming we have a set of polygons representing the water areas)
In order to solve these questions with a vanilla GeoServer, a client would have to first use WFS to gather all the geometries satisfying the base conditions (e.g. find the National Bank Subsidiaries), load, unite them and then issue a second request to the server in order to get the data from the other layer (e.g. the bus stops within 100m from the previously loaded points).
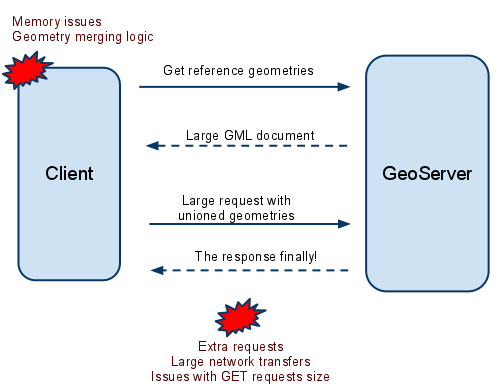
Round trips without cross layer filtering
The querylayer module¶
The querylayer extension, already installed in the workshop GeoServer instance, provides three new filter functions that can be used to avoid the client/server extra round trips, and have the server handle the secondary geometries collection instead.
| Name | Arguments | Description |
| querySingle | layer: String, attribute:String, filter:String |
Queries the specified layer applying the specified (E)CQL filter and returns the value of attribute from the first feature in the result set. The layer name should be qualified (e.g. topp:states), the filter can be INCLUDE if no filtering is desired |
| queryCollection | layer: String, attribute:String, filter:String |
Queries the specified layer applying the specified (E)CQL filter and returns the list of the values from attribute out of every single feature in the result set. The layer name should be qualified (e.g. topp:states), the filter can be INCLUDE if no filtering is desired. Will throw an exception if too many results are being collected (see the memory limits section for details) |
| collectGeometries | geometries: a list of Geometry objects |
Turns the list of geometries into a single Geometry object, suitable for being used as the reference geometry in spatial filters. Will throw an exception if too many coordinates are being collected (the results of queryCollection cannot be used as is) |
These filter functions can be used directly in CQL filters, OGC filters and SLD, meaning they are available both from WMS and WFS.
Finding all polygonal landmarks crossing a trail¶
The following map , obtained using the WMS reflector to keep the URL short, shows all polygonal landmarks and trails in Boulder (trails are visible when zooming-in due to scale dependencies):
http://localhost:8083/geoserver/geosolutions/wms/reflect?layers=geosolutions:bplandmarks,Trails&format=application/openlayers&width=512&height=512&BBOX=-105.31,39.97,-105.26,40.2
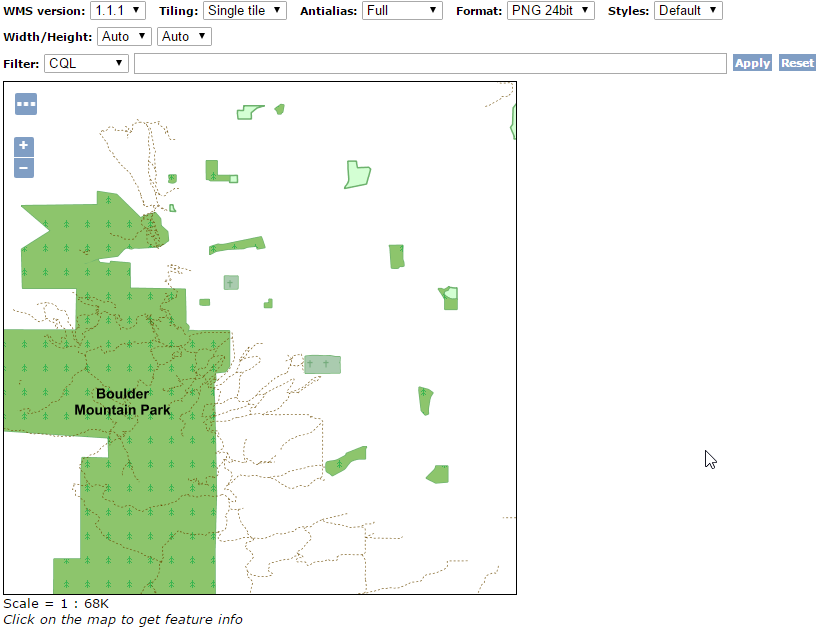
Polygonal landmarks and trails in Boulder
Now, let’s assume we want to find all polygonal landmarks crossing any trail using the above filter functions.
The first step would be to locate all the trails and extract their geometry attribute (the_geom):
queryCollection('Trails', 'the_geom', 'INCLUDE')
The above builds a list of geometries that we want to turn into a single MULTILINESTRING, in order to use it as a reference for a INTERSECTS filter. So we’ll call collectGeometries:
collectGeometries(queryCollection('Trails', 'the_geom', 'INCLUDE'))
Now that we have all the trails in a single geometry object we can use it to build a intersection filter with the polygonal landmarks:
INTERSECTS(the_geom, collectGeometries(queryCollection('Trails', 'the_geom', 'INCLUDE')))
Since the map contains two layers and we only want to filter on the first, the final CQL filter used in the GetMap request will be:
INTERSECTS(the_geom, collectGeometries(queryCollection('Trails', 'the_geom', 'INCLUDE')));INCLUDE
The result is that only two polygonal landmarks, the Boulder Mountain Park, and the smaller Buckingham Park, cross any trail:
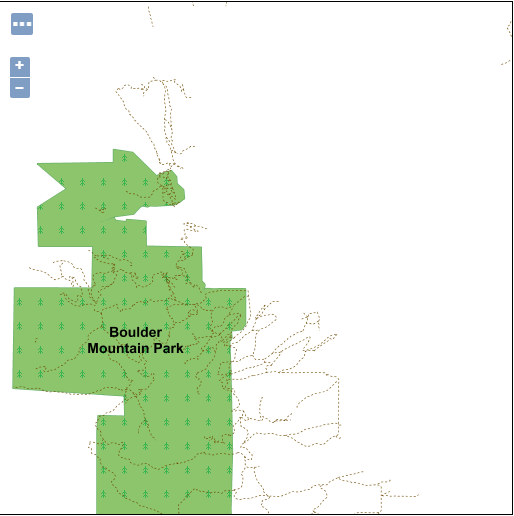
Polygonal landmarks intersecting trails in Boulder
Finding all buildings located inside a park¶
In this case we’ll start with this map:
http://localhost:8083/geoserver/geosolutions/wms/reflect?layers=geosolutions:bplandmarks,bbuildings&format=application/openlayers&width=512&height=512&&BBOX=-105.29,40.01,-105.28,40.02
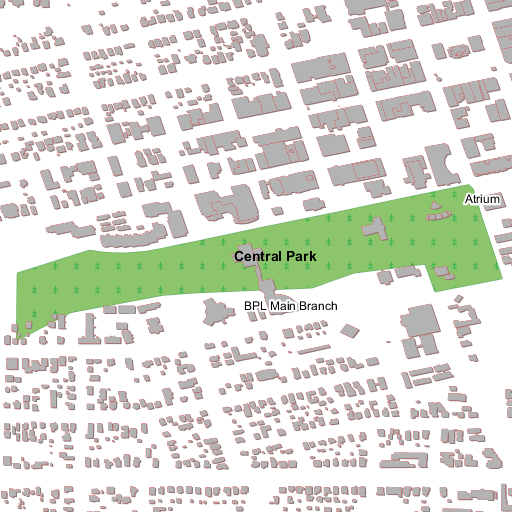
Buildings and parks in Boulder
The filter construction is similar to the previous case, but this time we need to collect geometries only from parks, which have a MTFCC attribute equals to K2180:
INCLUDE;INTERSECTS(the_geom, collectGeometries(queryCollection('bplandmarks', 'the_geom', 'MTFCC = ''K2180''')))
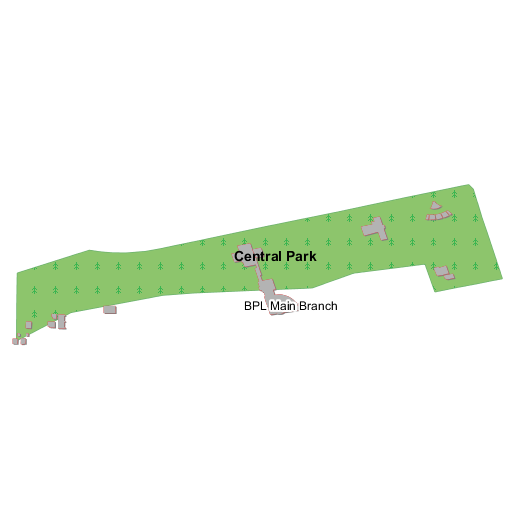
Buildings inside parks in Boulder
Finding all buildings close enough to the Boulder County Courthouse¶
In this case we want to find all the buildings close to the Boulder County Courthouse. The reference map this time is:
http://localhost:8083/geoserver/geosolutions/wms/reflect?layers=geosolutions:bptlandmarks,bbuildings&format=application/openlayers&width=512&height=512&&BBOX=-105.28061758059,40.016146865234,-105.27475307863,40.021151240234
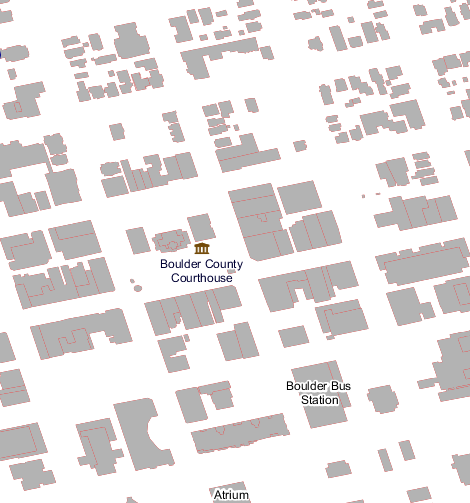
Boulder County Courthouse surrounded by buildings
This will extract a single geometry that we’ll use as a reference, so this time we are going to use the querySingle function instead, and use the DWITHIN function to locate all buildings within 400 feet from the courthouse:
INCLUDE;DWITHIN(the_geom, querySingle('bptlandmarks', 'the_geom', 'FULLNAME = ''Boulder County Courthouse'''), 400, feet)
and the resulting map is going to be:
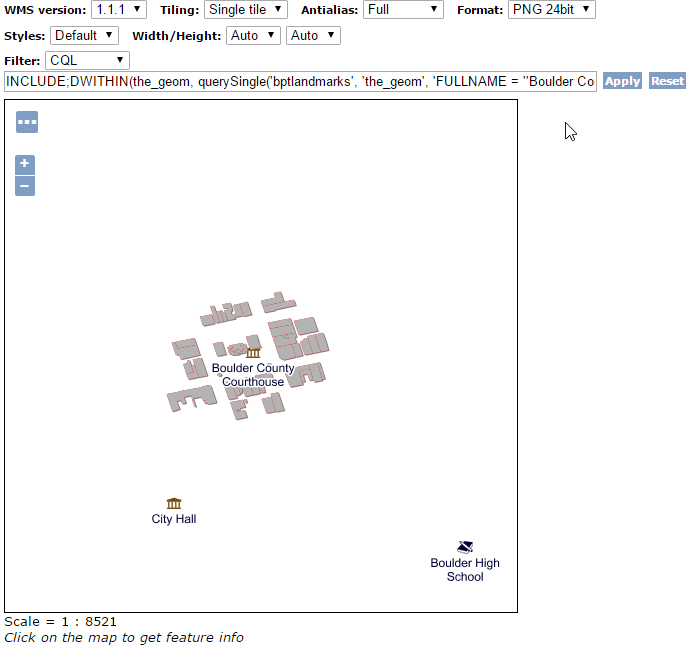
Buildings close to the Boulder County Courthouse
